When you’re injured in a car accident, life can turn upside down in an instant. Medical bills start to pile up, your ability to work and earn a living may be impacted, and the pain and trauma of the experience can weigh heavily on you and your loved ones. At West Coast Trial Lawyers, we understand what you’re going through, and our compassionate, experienced car accident attorneys are here to help you every step of the way.
Why Choose West Coast Trial Lawyers?

506 REVIEWS
This is my first time needing a lawyer and I couldn't believe how helpful these guys were! They were very professional, quick and easy to work with! I even came to the office to pick up my check and the receptionist was very nice and even offered me water (it was a hot day). I would 100% recommend this team and come back for their services!
Nancy N.

308 REVIEWS
oast Trial Lawyers. Each attorney who has worked on my case showed professionalism, good communication skills, and compassion towards me. I was also satisfied with the pay I received for each case.
Micheal Swarz

308 REVIEWS
Exceptional service from start to finish! The team at West Coast Trial lawyers handled my personal injury case with professionalism, compassion, and expertise. They kept me informed every step of the way and fought tirelessly to ensure I received the compensation I deserved. I highly recommend their services to anyone in need of legal representation for personal injury cases. 5 stars!
Andre Hinojos

308 REVIEWS
I was involved in car accident last summer while taking my kid to school. It was my first accident so I was extremely nervous and scared. After venting out several law firms, I went with West Coast Trial Lawyers. From the start, till the very end, I was always connected and in touch with my attorney, the process was a lot easier than I thought and I am happy to say everything went better than expected with my case!! Thank you to the entire staff!
Charles Thompson

497 REVIEWS
This is a great firm that gets it done. When my brother was killed in an auto/bike accident we contacted West Coast Trial Lawyers and they handled our case and even got us a really great setttlement based on the situation and circumstance. We know no one could have done a better job.
Meck Giinan
With over 20 years of experience handling car accident cases, we know how to build strong claims and negotiate aggressively with insurance companies to secure the maximum compensation you deserve. Led by Harvard-educated attorney Neama Rahmani, our team brings top-tier legal expertise and a relentless commitment to advocating for car accident victims. Our law firm has recovered over $1.7 billion for our clients, and we’re ready to fight for you.
When you work with our auto accident lawyers, you don’t pay a dime unless we win your case. We work on a contingency fee basis, so you can focus on your recovery without worrying about upfront costs. Let us take on the legal burdens so you can begin rebuilding your life.
Get the support you need to move forward. Speak to a car accident lawyer today by calling (213) 927-3700 or use our online contact form for a FREE consultation!
How Our Car Accident Lawyers Can Help You Win Your Case
Many people wonder, “Do I really need a car accident attorney?” While it’s not legally required, having a car crash attorney by your side is highly recommended. Handling a car accident or personal injury case on your own can be overwhelming, especially while managing medical bills, lost wages, and the stress of recovery. Without a personal injury attorney, you risk missing crucial deadlines, underestimating the value of your claim, or accepting a low settlement from the insurance company.
Our seasoned experienced car accident attorneys know the ins and outs of car accident cases. We’ll handle every detail—from helping car accident victims with gathering evidence, communicating with insurance companies, and calculating your true losses to negotiating the highest possible compensation. Let us protect your rights and ensure you get the outcome you deserve, so you can focus on healing and rebuilding.
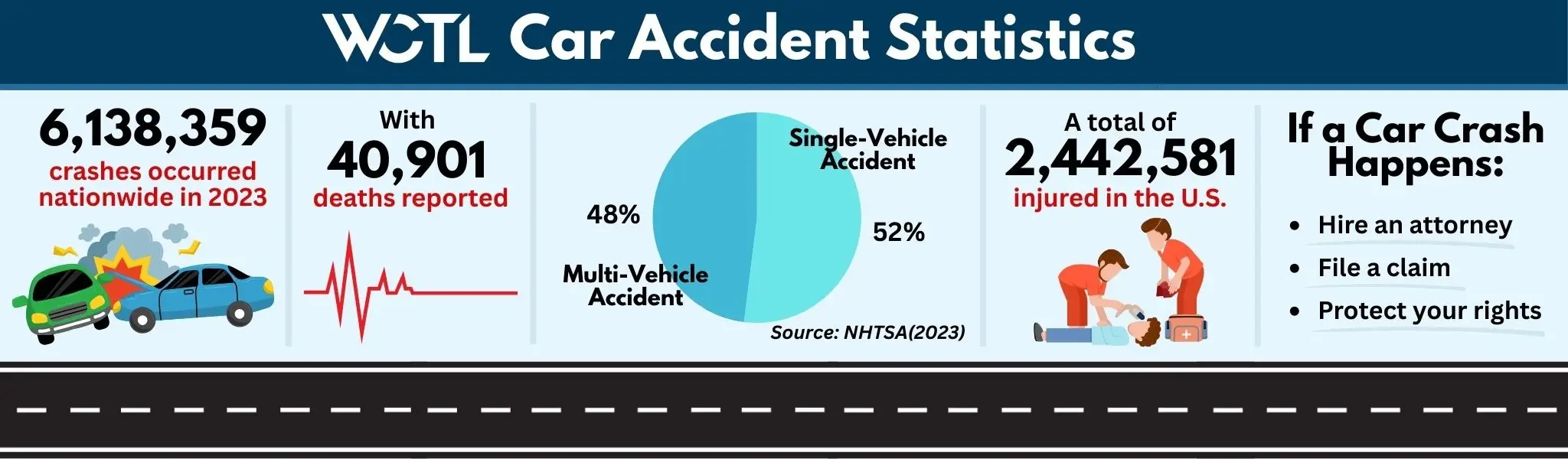
Car Accident Statistics
According to a 2023 Motor Vehicle Traffic Crash report by the National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA), there were an estimated 6,138,359 police-reported traffic crashes, and out of that 40,901 people were killed and an estimated 2,442,581 people were injured. Meanwhile, a car accident data report by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) states that the U.S. had a total of 40,901 deaths from motor vehicle accidents in 2023, with 52% of deaths occurring in single-vehicle crashes.
With such a staggering number of serious injuries and fatalities from car accidents, it is more important than ever before to properly follow road rules and procedures to ensure that you do not accidentally become involved in a car wreck. However, should accidents happen for whatever reason, it is important to file a personal injury claim with an attorney to ensure that you would be able to financially recover from such a common accident.
Types of Car Accidents We Can Help With
We are here to represent motorists who have been harmed in car accidents. Our clients have won substantial settlements because our team digs deeper for information regarding their case. While every car accident case is different, it is important that accident victims try to understand their situation as much as possible, so they can provide their attorneys all of the necessary information.
Single Car Accidents
A single-vehicle car accident is when there is only damage inflicted to one vehicle and these types of accidents occur when the driver either loses control of their vehicle or swerves out of control in an attempt to avoid crashing into another vehicle or person.
According to a 2023 Fatality Facts report by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, about 52% of fatal car accidents are derived from single-vehicle accidents nationwide. Due to the nature of this type of car accident, the liability will tend to fall onto the driver, in motor vehicle collisions, however, if there is substantial evidence that proves that the accident scene was caused by another negligent party such as recklessly creating a road hazard then they can be potentially held liable for all damages.
Multi-Car Accidents
A multi-vehicle accident is when two or more vehicles are involved in a car crash either due to the negligence or ill intent of one driver. Multi-car traffic accidents can happen anywhere, but they typically occur in highly congested locations where multiple drivers are in close proximity from one and another. Other factors that may cause this accident include speeding, tailgating, drunk driving, distracted driving, drowsy driving, and even road rage.
Due to the nature of this type of accident, multi-vehicle accidents are often the most contested between those involved because the party that claims responsibility will be liable for all damages and their car insurance premiums will drastically go up as a result. In addition, a 2023 Fatality Facts report by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety has discovered that roughly 48% of traffic fatalities are from multi-car accidents and pileups. So should a loved one have perished in a car accident, it would change the nature of the case from a motor vehicle accident to a wrongful death lawsuit.
Head-On Collisions
A head-on collision is a type of car accident where the front ends of two vehicles traveling in opposite directions strike one another at a significant speed. This type of auto accident is highly likely to cause serious and possibly fatal injuries due to the amount of force inflicted onto both drivers and their passengers.
According to a 2023 Type of Crash Overview by the National Safety Council, nearly 30% of head-on collisions were fatal. While the liability in these motor vehicle collision cases are usually on the negligent driver who caused the car wreck, there are instances where faulty mechanical parts were the leading cause of the accident and the car manufacturer or the mechanic who last worked on the vehicle can be held liable for their negligence. Should that be the case, a thorough investigation needs to be conducted in order to determine who is liable for the damages that have occurred.
Rear-End Accidents
Rear-end accidents are a frequent occurrence on U.S. roads, with car crashes happening when one vehicle collides with the back of another. These types of car accidents can vary in severity, from minor fender benders to serious collisions, depending on the speed and circumstances involved.
Common causes of rear-end accidents include distracted driving, speeding, and tailgating. If you find yourself involved in a rear-end accident, it is crucial to seek the assistance of an experienced auto accident lawyer. They can help you navigate the complexities of your case and ensure you receive the compensation you deserve for any injuries or damages sustained.
T-Bone Accidents
T-bone accidents, also known as side-impact collisions, occur when the side of one vehicle is struck by the front or rear of another vehicle. These broadside collisions often result in severe injuries due to the limited protection on the sides of vehicles.
T-bone accidents frequently happen at intersections and are commonly caused by drivers failing to yield, running red lights, or speeding. If you have been involved in a T-bone accident, it is essential to consult an experienced car accident lawyer.
The Importance of Finding a Local Car Accident Lawyer
When you’ve been involved in a car accident, hiring a local attorney can make all the difference in navigating your case effectively. Local lawyers understand the specific laws, regulations, and court systems in your area, giving you an edge when it comes to building a strong case. Beyond legal knowledge, local attorneys often have connections with local experts, investigators, and resources that can be crucial to your claim.
Here are just a few of the benefits of working with a local car accident lawyer:
- In-depth knowledge of local laws: Each state has its own nuances when it comes to handling car accidents, from traffic patterns to court procedures.
- Familiarity with local courts and judges: A local attorney knows the preferences and tendencies of judges and other legal professionals in the area.
- Accessibility and personalized service: Meeting your attorney in person can provide peace of mind and foster clear communication throughout the process.
If you’re looking for an experienced local car accident lawyer, we proudly serve clients in:
By choosing a lawyer who knows your city, you’ll receive the tailored support and legal guidance you need to achieve the best possible outcome for your claim. Don’t settle for generic legal representation—work with someone who understands the unique challenges and opportunities in your local area.
Common Types of Car Accident Injuries
Approximately 3.2 million Americans die in car accidents yearly and to some people’s surprise, there are many car accident injuries that are left undiagnosed or untreated due to people’s aversion to expensive medical bills. This not only leaves their car accident victims suffering long-term effects of serious injuries, but they are forced to live their lives without the proper care or compensation they need to make a full recovery.
Knowing the most common injuries in the event of a car accident can help you understand the importance of seeking immediate medical attention and legal guidance if you’re involved in a collision.
Head Injuries
- One of the most common injuries in car accidents, head and brain injuries are described as a brain dysfunction that is caused by a forceful bump, blow, or jolt to the head.
- They are typically derived from the force and acceleration in a car accident, and even with protective measures such as airbags and seatbelts in place, drivers and passengers can still suffer head injuries.
- While the extent of the injury will be largely dependent on the nature of the accident, the brain can be injured in a number of ways, from light bruising to torn brain tissue.
- In the event of a severe car accident, brain injuries can become fatal especially if it is not properly treated.
Spinal Cord Injuries
- A spinal cord injury is referred to as damage either to the spinal cord or to the bundle of nerves around the spine.
- Due to the spine’s limited ability to absorb heavy impacts and force, they are a common injury found in motor vehicle collisions and can cause quite a bit of discomfort to the spine and the lower back.
- In severe instances, it can even affect one’s motor functions and can cause lifelong nerve damage such as paralysis.
- Even a minor collision can still cause quite a bit of discomfort and can drastically affect your mobility, how you carry yourself at work, and your quality of life.
Internal Injuries
- One of the most unsuspecting and common car accident injuries, internal injuries are defined as internal bleeding and damage to organs.
- This type of injury is typically caused by a sudden impact force from another moving vehicle.
- While the severity of these injuries will vary on the impact force, it can potentially cause injuries such as broken ribs, ruptured organs, and even bone fractures.
- Even if an accident victim emerges from a car accident appearing fine, they may still have suffered internal injuries.
Emotional and Psychological Trauma
- It’s not uncommon to experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, depression, or other emotional distress following an accident.
- While the psychological impact will vary on a case-by-case basis, there is no shame to admit that the accident has had a profound impact on you.
- If the aftermath of a car accident is making it difficult for you to live your day-to-day life, it is highly recommended to seek aid from professional so they can help get through this traumatic experience.
What To Do If You Have Been Involved in a Car Accident?
Determining Liability In a Car Accident Claim
Determining liability after a car wreck can be difficult, especially if more than one party is involved. You will need to gather information and evidence to have solid proof to determine who committed acts of negligence. Negligence is referred to as a form of reckless or careless behavior that has led to the accident in question. It is against the law to perform negligent actions as it can pose a safety risk to others nearby. To successfully prove negligence, you will have to present the following three elements:
- The defendant owed you a duty of care
- The defendant breached his or her duty of care through negligence
- The defendant’s negligence was the primary cause of the injuries you sustained
What Is a Duty of Care?
A duty of care is defined as a legal obligation that is required for a person to follow in order to prevent foreseeable harm from happening to others. For example, in the case of a car accident, every driver on the road has a duty of care to ensure that they are paying on the road and are obeying traffic laws accordingly. If a driver was speeding or driving while under the influence and ultimately caused a car accident, then that driver will be held accountable for any and all damages.
With that in mind, if you have been involved in a car accident, it is important to take account of every detail leading up to the accident and should you require additional assistance, car accident lawyers are able to help determine liability and who has broken their duty of care.
Available Damages In a Car Accident
When it comes to recoverable damages in a car accident claim, the severity and scale of the accident in question will help determine what kind of damages accident victims can recover. From what is typically seen in car accidents, injured victims can either recover economic, non-economic, and possibly even punitive damages for a car accident. While the awarded compensation will greatly depend on the circumstances involved in your case such as how well the negotiations goes through between you and the insurance company, it is important to familiarize yourself with how these damages differ from each other to serve as a point of reference for your car accident injury claim.
Economic Damages
Economic damages are referred to as calculable expenses that have arisen due to the accident in question. For example, costs such as medical expenses, property damage, lost wages, future medical bills, and quality of life adjustments are all calculable expenses that a victim can be compensated for being a victim to an unfortunate car accident. They are calculated by determining the amount of out-of-pocket losses a victim has or will expect to incur as a result of their injuries and are designed to make car accident victims financially whole.
Non-Economic Damages
Non-economic damages are referred to as incalculable expenses that have occurred as a result of the car accident in question. These damages are thought of as subjective in nature thus the value will vary on a case-by-case basis. For example, loss of consortium, emotional distress, loss of enjoyment of life, and pain and suffering are all subjective and will affect a car accident victim differently. As such, a car accident attorney will need to prove that the car accident has had a profound effect on their client and their lifestyle in order to recover non-economic damages for them.
Punitive Damages
Punitive damages are separate from compensatory damages (economic and non-economic) and are intended to punish a wrongdoer for their negligent or deliberately harmful behavior. While punitive damages are rarely issued, it is meant to serve three purposes, to deter similar accidents from occurring in the future, set legal precedence, and to give the victim and their family justice and closure. For example, driving without a license, reckless driving, hit and runs, and intentional acts of violence are all punishable.
How Long Do I Have to File a Car Accident Claim?
In the United States, the amount of time you are given to file a car accident claim will vary based on your state’s statute of limitations. For most places, the most common duration is two years from the date of the accident. Property damage claims may follow a similar time limit, though some states may allow a slightly longer period when it comes to vehicle damage. But keep in mind, these timelines will differ by state, so the exact deadline will depend on where the collision happened.
Exceptions to the Statute of Limitations
There are some situations where the time frame to file a claim might be different:
- Claims Against Government Entities: If your accident involved a government vehicle or hazardous road conditions caused by a government agency, you may have as little as six months to file a claim.
- Minors: If the injured person is under 18, the statute of limitations typically begins when they turn 18.
- Delayed Discovery: In rare cases, if you didn’t discover your injury right away, the clock starts ticking from the date you became aware of it.
What If I Get Accused of Partly Causing My Car Accident?
If you are being accused of partly causing your car accident, comparative negligence laws will kick in. Under this regulation, your compensation will be adjusted based on your percentage of fault. For instance, if you are found to be 20% responsible for the incident and your total damages equal $100,000, you may still be entitled to $80,000. The exact impact will depend on your state.
Some states follow a “pure” comparative negligence rule, allowing you to recover damages even if you are mostly at fault for the car accident, though your amount will be reduced accordingly. However, other states comply with a “modified” comparative negligence rule, barring you from receiving compensation if you are 50% or 51% accountable.
Additionally, a smaller number of states adopted contributory negligence rules, where even if you are 1% at fault, you will be restricted from recovery entirely. Which is why, no matter what state you live in, it is always recommended to seek out an experienced attorney for guidance.
West Coast Trial Lawyers Is Here to Help
If you have sustained injuries in a car accident as a result of someone else’s negligence or ill intent, you may be able to hold the at fault driver responsible for their actions and recover financial compensation for your damages. As a car crash can produce devastating injuries for everyone involved, it is vital that you hire an experienced auto accident lawyer who will serve as your personal legal representative and fight for you and your rights.
At West Coast Trial Lawyers, our team of car accident attorneys are ready to take on your case and serve as your personal legal representative. We are a law firm that specializes in personal injury lawsuits and with over 20 years of legal experience, our compassionate team of attorneys handle every car accident case with the utmost care and respect that it deserves. As a result of their dedication, they are confident that they can get you the maximum compensation you deserve for your losses.
We have recovered over $1.7 billion in financial compensation for our clients and we are prepared to fight for you. Whether you have been involved in a serious car wreck or a minor one, our talented team of car accident attorneys have seen them all and they are available 24/7 to answer any questions or concerns you may have regarding your case.
We run on a contingency-fee basis, meaning you pay no fees until you win. To schedule a FREE case evaluation, you can get in touch with us by calling us at (213) 927-3700 or by filling out our quick online contact form.
Frequently Asked Questions About Car Accidents
Can You Sue for a Car Accident?
In the event of an auto accident, if you are not the one who has caused the accident in question, then you are able to sue the responsible party for any and all damages you have sustained. However, it is recommended to hire experienced car accident attorneys to handle your case, because accident attorneys understand the legal process of a car accident case and will do everything in their power to ensure that their clients are properly compensated for their injuries.
What Happens if a Driver Doesn’t Have Car Insurance?
If a driver does not have car insurance in the United States, what happens will depend on your own coverage and your state’s laws. If the uninsured driver triggers the collision, you may be eligible to recover compensation through your own uninsured motorist (UM) coverage. This is made for circumstances where the at fault driver has no insurance.
In some states, this coverage is required, and in others, it is optional, but can be included in policies. Such coverage can help compensate for bodily injury, lost wages, pain and suffering, property damage, and hit-and-run accidents.
Depending on the severity of the accident, uninsured drivers may even have their vehicles impounded and their driver’s license suspended. Should you become involved with an uninsured driver, it is important to seek legal representation to ensure that the car accident in question is settled properly and accordingly.
What Are the Most Common Mistakes When Filing an Accident Claim?
There are many common mistakes that can be made when filing an accident claim and while it is understandable to make some missteps along the way, it is imperative that accident victims do not constantly make a series of mistakes. With that in mind, here are some of the most mistakes that are made:
- Not seeking medical attention right away
- Failing to call the police
- Admitting fault or apologizing
- Not gathering enough evidence
- Delaying the claims process
- Accepting the first settlement offer
- Not consulting with an attorney
- Posting on social media
- Failing to keep records
How Much Can You Sue for Pain and Suffering From a Car Accident?
There is no fixed dollar amount for pain and suffering in U.S. car accident cases. The value will depend on the intensity of your injuries, the duration of your recovery, and how the incident has affected your overall daily life. Pain and suffering damages fall under non-economic losses.
They may compensate you for physical pain, emotional distress, anxiety, and loss of enjoyment of life. Since these do not come with receipts, there is no actual universal formula that guarantees a certain payout. The amount you can sue for will be based on the facts presented in your case, the evidence provided, and the laws enforced by your state.
How Long Does It Usually Take to Settle a Car Accident Lawsuit?
In the United States, a car accident lawsuit may take anywhere from a couple of months to a few years to settle depending on the circumstances involved. Minor cases may be resolved within six to nine months, and can be sooner if medical treatment is completed quickly and the insurance company is willing to cooperate.
More complex situations involving serious bodily harm, disputed fault, or significant damages can take one to two years or longer. If the case heads to litigation, the timeline may extend the legal process.
What to Do if You Are Accused of Causing a Car Accident?
If you are accused of a car accident, but know for a fact that the other party was partially liable, it is important to stay calm, document the accident scene as much as possible, and avoid discussing fault.
Gathering detailed documentation, such as photos, witness statements, and video evidence, can help you build a strong case to protect you against liability allegations. In addition, by avoiding comments that could be interpreted as fault during conversations with insurance companies, you can minimize the liability that you are accused of. Stick to the facts, have your attorney handle these discussions, and let the investigation determine fault.
What Type of Attorney Handles Car Accidents?
A personal injury attorney handles car accident cases. They focus on representing victims who were harmed as a result of someone else’s negligence, and they work to recover compensation for losses, like medical bills, lost wages, and pain and suffering.
Many personal injury lawyers manage a wide variety of motor vehicle-related accident cases, including car, motorcycle, truck, and pedestrian collisions. They will directly communicate with insurance companies, investigate the incident, gather evidence, and if needed, file a lawsuit and represent clients in court. If a crash leads to a fatality, a wrongful death attorney will be the one to manage such a case.
Is It Worth Hiring an Attorney After a Car Accident?
It is usually worth hiring an attorney after a car accident, especially if you sustained injuries or there is a dispute going on about who is at fault for causing it. Insurance companies will try to minimize payouts, and an experienced car accident attorney can help protect your claim, manage communications with insurers, and pursue full compensation on your behalf.
For minor circumstances that involve no injuries and minimal property damage, hiring a lawyer could be beneficial if your condition worsens over time or the insurance company denies your claim. Ultimately, consulting with a legal expert can make a big difference with the outcome of your car accident lawsuit.
Is It Worth Suing Over a Car Accident?
Suing over a car accident may be worth it if you suffered serious injuries and are met with costly medical bills, lost wages, and unfair settlement offers. Many cases can be resolved through negotiations. However, a lawsuit can increase the pressure and result in a more reasonable payout. If your damages are minimal and fully covered, suing may not be the best path to take. The decision will primarily depend on the extent of your losses and if the potential recovery justifies the time spent and legal process involved.
Should I File a Claim or Get a Lawyer First?
You should report the accident to maintain your coverage. But, giving statements or answers to in-depth questions from an insurance adjuster without legal guidance can unintentionally harm your personal injury claim. Insurance companies will try to use your words against you to reduce payout, shift blame, or argue that your damages are less serious than what you initially stated, which can end up minimizing your recovery.